AFM Testing Cases
Module on Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
By E. A. Leone
Brief History
- Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM)
- Developed in 1982 by Binning, Rohrer, and Weibel at IBM Zurich,Switzerland
- Binning and Rohrer won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1986
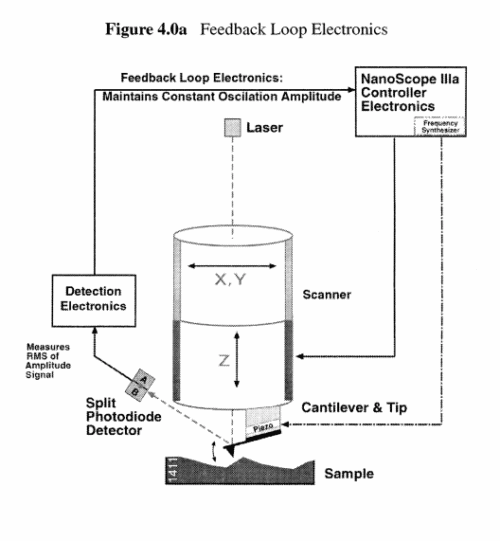
- Atomic Force Microscope (AFM)
- Developed in 1986 by Binning, Quate, and Gerber, as a collaboration between IBM and Stanford University
Definitions
- Scanning Probe Microscope (SPM)
- Family of microscopies where a sharp probe is scanned across a surface and the probe/ sample interactions are monitored
- There are Two Major Forms of SPM
- STM
- AFM
- There are 3 Major forms of AFM
- Contact Mode AFM
- Non-Contact mode
- Tapping Mode
A number of SPM Probes are Available to use for Nanotechnology Characterization
- Contact mode AFM
- Lateral Force
- TappingMode AFM
- Non-contact AFM
- Force-volume imaging
- Magnetic Force
- Electric Field
- Surface Potential
- Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
- Operation in fluid
- Phase Imaging
- Quadrex3
- Scanning Capacitance
- Conductive AFM
- Nanolithography
- NanoManipulation
- 4-point probe
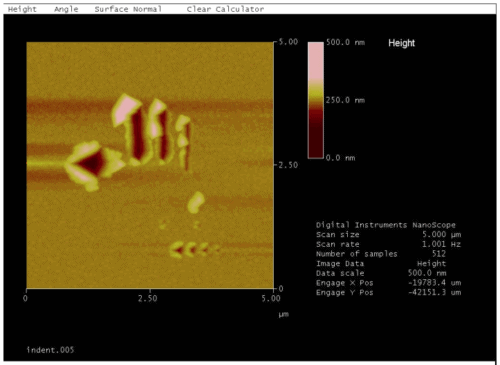
- NanoIndentation
- Scanning Spreading resistance
- Torsional Resosnance Mode
AFM Summary
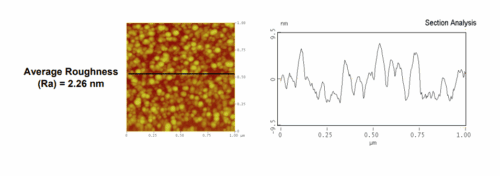
- AFM used to observe the surface morphology at high magnifications.
- Accurate height (roughness) measurements can be made.
- A large range of “modules” are available to measure a number of surface properties.